This Week in Earnings – Q2'25
Materials Sector Beat
Our thought leadership this week addresses:
- Key Events
- Earnings Snap, covering the S&P 500 stats to date
- Spotlight on Materials in The Sector Beat
Key Events
Tariffs / Trade Policy
- President Trump’s updated “reciprocal” tariffs took effect on Thursday, imposing higher duties on many of the country’s trading partners’ exports to the U.S. Meanwhile, though the Administration has suggested a deal with China is near, a trade agreement has yet to be reached as the August 12 expiration of their 90-day truce approaches. (Source: CNBC)
- Trump raised India tariffs to 50% over Russian oil purchases. Trump implemented an additional 25% tariff on India, days after he already imposed a 25% levy on the major trading partner. The new tariffs are set to go into effect in 21 days, according to the order, while the previously announced 25% tariffs took effect on Thursday. (Source: CNBC)
- Trump said he will impose a 100% tariff on imports of semiconductors and chips, but not for companies that are “building in the United States”. Specifics about the plan, such as how much U.S. manufacturing a company needs to do in order to qualify for the tariff exemption, were not immediately clear. (Source: CNBC)
Monetary Policy
- The Bank of England cut by 25 bps as expected, lowering its key interest rate to 4.0% in a narrow 5–4 vote that followed an unprecedented second round of committee voting amid stubborn inflation and softening growth. (Source: Bank of England, CNBC)
Labor Market
- U.S. initial jobless claims rose 7,000 to a seasonally adjusted 226,000 for the week ended August 2, above economist forecast of 221,000 and the highest level since July 5. Continuing claims rose by 38,000 to 1.97 million in the week ended July 26, the highest since November 2021 as the ‘no-hire, no-fire’ trend remains intact. (Source: The Labor Department, Reuters)
- The Canadian economy unexpectedly shed 41,000 jobs in July, compared with economist forecasts for a 15,000 gain, though this followed June’s surprisingly strong 83,000 jobs increase. The unemployment rate held steady at 6.9%, better than economist expectations for a 0.1 point uptick to 7.0%. (Source: Statistics Canada)
S&P 500 Earnings Snap
90% of the S&P 500 has reported earnings to date
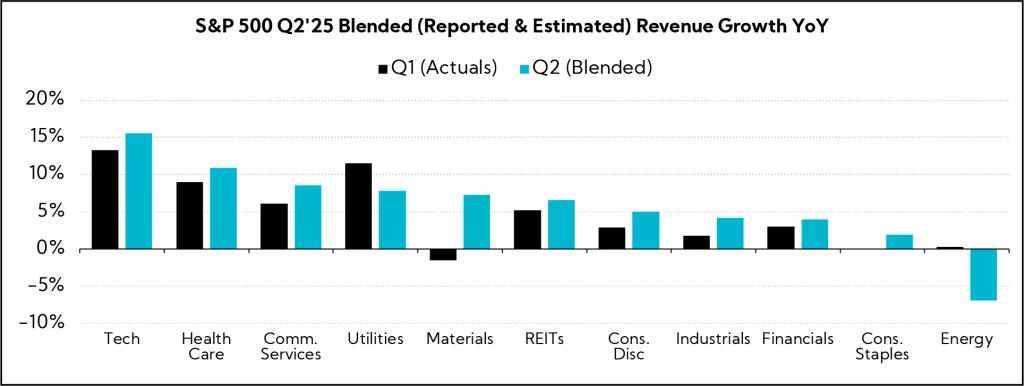
Q2'25 Revenue Performance
- 79% have reported a positive revenue surprise, above both the 1-year average (62%) and the 5-year average (70%)
- Blended revenue growth (combines actual reported results for companies and estimated results for companies yet to report) is 6.2%
- Companies are reporting revenue 2.8% above consensus estimates, above both the 1-year average (+0.9%) and the 5-year average (+2.1%)
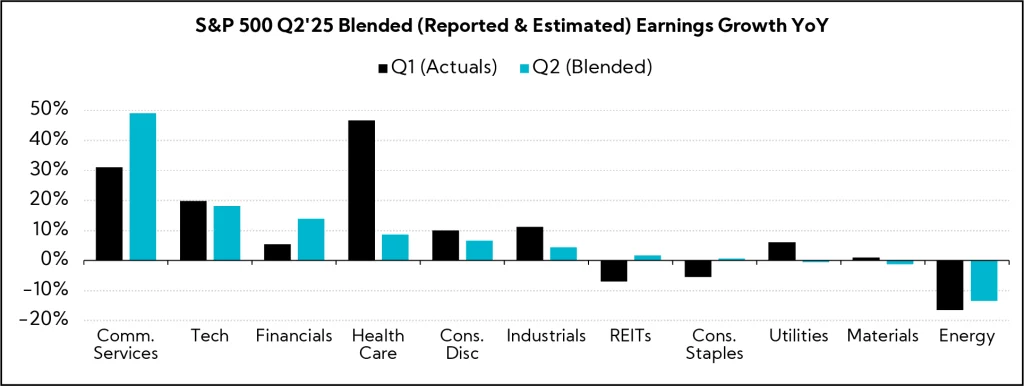
Q2’25 EPS Performance
- 80% have reported a positive EPS surprise, above both the 1-year average (77%) and the 5-year average (78%)
- Blended earnings growth (combines actual reported results for companies and estimated results for companies yet to report) is 13.2%
- Companies are reporting earnings 8.8% above consensus estimates, above the 1-year average (+6.3%), but below the 5-year average (+9.1%)
The Sector Beat: Materials
Materials Guidance Trends
We analyzed annual revenue and EPS guidance for a basket of U.S. Materials companies with market caps greater than $1B that have reported to date.1 Below are our findings.
For comparison purposes, we provide an “All-Company” benchmark, which tracks in real-time a basket of calendar year companies larger than $1B in market cap across all sectors that have reported earnings to date (n = 660).
Guidance Breakdown by Industry
| Industry | Number of Companies |
|---|---|
| Specialty Chemicals | 16 |
| Packaging & Containers | 9 |
| Metals & Mining | 3 |
| Construction Materials | 2 |
| Total | 30 |
Source: Corbin Advisors
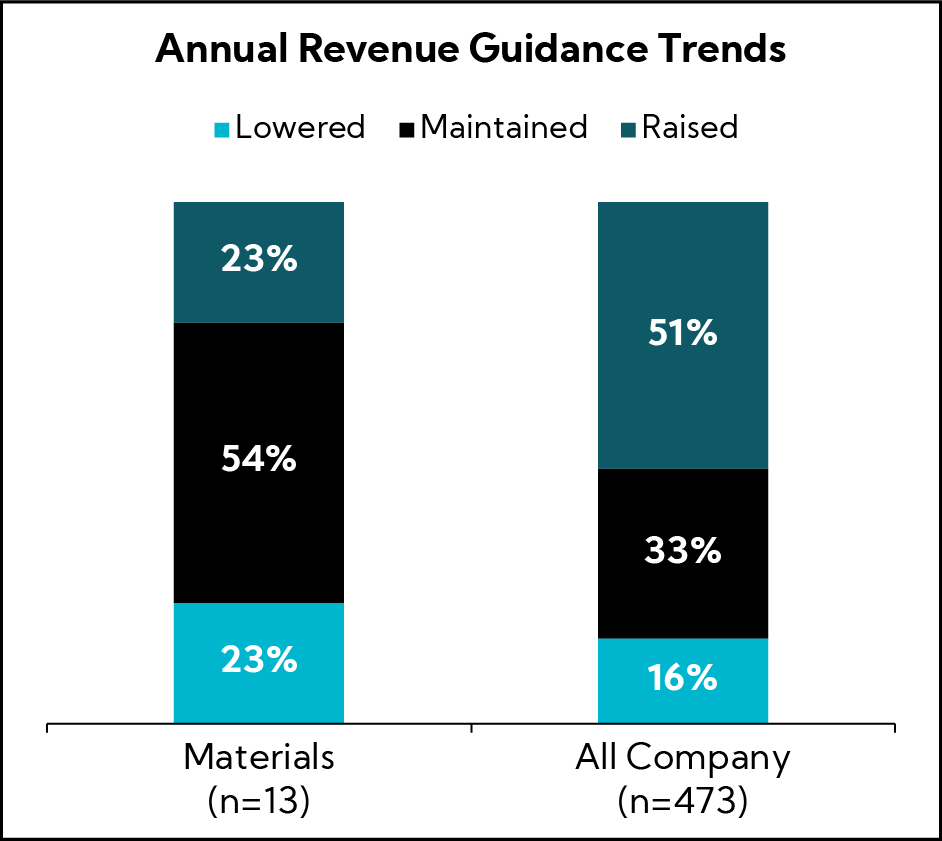
Revenue Guidance
To date, 23% of Materials companies have Raised annual revenue guidance, significantly below the All Company benchmark average. Notably, more than half Maintained guidance, compared with a third for the broader benchmark, where over 50% have Raised.
- Companies that Lowered guidance (n = 3)
- All lowered the top and bottom of the original range
- Average midpoint of 5.1% growth versus 7.7% last quarter
- Average spread increased by 50 bps to 5.4%
- Companies that Maintained guidance (n = 7)
- Average midpoint of -1.6% growth
- Average spread of 4.9%
- Companies that Raised guidance (n = 3)
- Raised both bottom and top of the original range
- Midpoint of 3.4% growth versus 0.9% last quarter
- Spread decreased by 80 bps to 1.8%
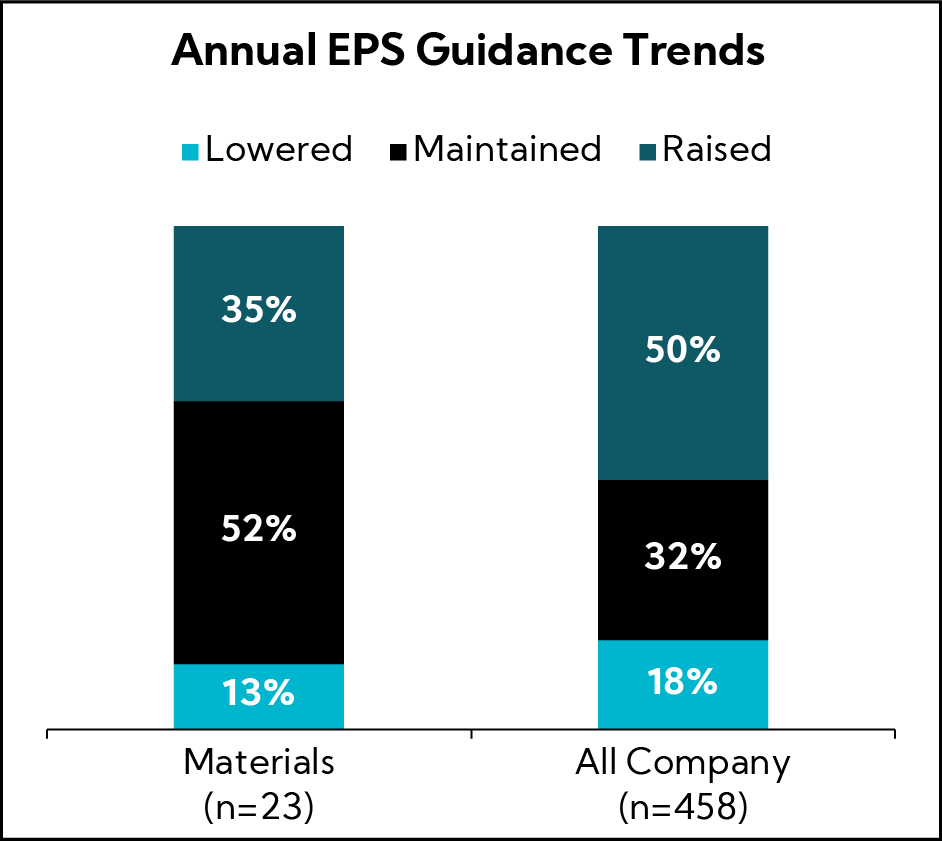
EPS Guidance
Similarly, far fewer Materials companies Raised annual EPS guidance relative to companies in other sectors with a greater proportion falling in the Maintained camp.
- Companies that Lowered guidance (n = 3)
- 66% lowered top and bottom of the original range; 33% lowered only top
- Average spread increased from $0.27 to $0.17
- Companies that Maintained guidance (n = 12)
- Average spread of $0.32
- Companies that Raised guidance (n = 8)
- 63% raised top and bottom of the original range, 25% lowered top while raising bottom, and 1 company (DuPont de Nemours) maintained top and raised bottom
- Average spread decreased from $0.25 to $0.20
Earnings Call Analysis
We analyzed earnings call prepared remarks and Q&A for this group and the broader Materials sector universe to identify key themes.
This earnings season, executive commentary reflects the ongoing challenges the sector continues to face as executives navigate a dynamic global trade environment and uneven demand across key regions. Indeed, while Q2 earnings for the S&P 500 have surpassed top- and bottom-line estimates at a healthy rate, 79% and 80%, respectively, just 60% of Materials have posted revenue beats, and a meager 48% have reported EPS above consensus – the lowest beat rates for any sector in the Index.
Demand trends remain mixed across end markets, with a number of companies pointing to a negative impact from tariffs on order rates, albeit with signs of improvement as the quarter progressed. Segments tied to housing, consumer-facing goods, and some industrial segments continue to face headwinds, while AI-related infrastructure, data centers, and select packaging categories show relative strength. Further, executives report customers are maintaining lean inventories and exercising caution in ordering, though some pockets, such as solar and wind, have seen a near-term boost from a rush to get ahead of expiring tax credits.
Tariffs and global trade policy remain front and center, with companies focused on mitigating impacts through surcharges, supply chain shifts, and pricing actions. While direct tariff costs are often described as manageable, concerns around secondary effects on demand and inflation remain prevalent.
In response to the uncertain macro environment, companies are doubling down on cost controls, expanding restructuring programs, and pulling back on capex to preserve cash. These efforts are especially pronounced among chemicals, as evidenced by Dow announcing a 50% dividend cut while further ramping its cost-cutting actions.
Globally, views vary across regions and end markets. Europe continues to struggle with weak industrial demand and macro volatility, while Asia faces persistent overcapacity and competitive pressures, largely from China, that are spilling into other export markets, including India. North America is characterized as stable, if not robust, and Latin America remains a relative bright spot.
Finally, several companies cite the recently passed OBBBA tax legislation as a tailwind, with bonus depreciation and R&D expensing expected to provide meaningful cash tax benefits and support future investment, though most are still evaluating the full impact.
Key Earnings Themes
Macro and Outlooks
Challenging, Dynamic Environment Drives Mixed Outlooks, with Tariff Uncertainty and Macro Volatility at the Fore
- Sherwin-Williams ($86.7B, Chemicals): “As we enter the second half, it is clear we continue to be in a softer-for-longer demand environment with further deterioration possible. Customer sentiment reflects continued uncertainty and hesitancy to invest, and consumer confidence remains mixed. To be clear, we expect no help from the market over the remainder of the year. As a result, we are revising our full year sales expectations downward.”
- PPG Industries ($23.7B, Chemicals): “Our results demonstrate the strength of our global business portfolio in an increasingly dynamic macro environment. Looking ahead, I am genuinely excited about our sales and earnings growth momentum for the second half of the year and beyond. We are reiterating our full year guidance and we have a clear path to achieve it.”
- Dow ($15.3B, Chemicals): “The prolonged downcycle our industry has been experiencing was further amplified this quarter by heightened trade and geopolitical uncertainties, which have strained profitability across our industry. We announced this morning that we would implement a 50% dividend reduction. Given the current lower-for-longer earnings environment and the lack of a clear line of sight to a recovery for our industry, this is the most prudent way to maintain financial flexibility and maximize long-term value for shareholders.”
- Avery Dennison ($13.1B, Containers & Packaging): “Given the near-term uncertainty, we are taking a cautious approach to forward expectations and expect Q3 EPS to be comparable to prior year. We are prepared for a range of scenarios and will continue to leverage our proven playbook to safeguard earnings, while driving key initiatives to deliver strong profitable growth. While we’re not giving guidance for the full year, we do anticipate returning to earnings growth compared to prior year in Q4, assuming no significant shift in the macro.”
- Crown Holdings ($11.5B, Containers & Packaging): “Q2 performance came in better than anticipated. We’re mindful of the potential impacts that tariffs may have on the consumer and industrial activity. Considering the strong first half and the potential impacts from tariffs, we’re raising our guidance for the full year. The widest part of the range given is Q4, and that’s really a lot to do with tariff uncertainty.”
- Cabot ($4.3B, Chemicals): “Based on Q3 performance and our outlook for Q4, we are reaffirming our expected full-year outlook. This reflects YoY EPS growth for fiscal 2025 in what is a very weak environment, driven by the uncertainty from tariffs and soft global macroeconomic conditions. At current demand levels, we would expect to be in the middle to lower end of the range. If the more recent tariff announcements were to translate into higher demand in fiscal Q4, we’d expect to be higher in the guidance range.”
- TriMas ($1.4B, Containers & Packaging): “Following a strong first half of the year, we are increasing both our full year sales and earnings guidance supported by continued strength in our Aerospace business and positive trends within Specialty Products. While we expect much of our positive momentum to continue, the changing tariff environment continues to present uncertainty in customer order patterns and consumer demand, which we continue to monitor.”
Mixed Demand Signals
Cautious Ordering Patterns, Lean Inventories, and Choppiness Persist; Housing, Consumer-facing, and Some Industrial Segments Weaker, While Infrastructure, AI, and Defense Show Continued Strength
- Sherwin-Williams ($86.7B, Chemicals): “We began the year by telling you that we were operating in a very choppy demand environment. As the quarter progressed, demand momentum remains stalled and, in some areas, deteriorated further, notably in new residential, DIY and Coil Coatings end markets.”
- DuPont de Nemours ($30.4B, Chemicals): “Q2 saw continued strength in electronics, driven by AI technology demand in both Interconnect Solutions and Semi, and strong volume growth in healthcare and water. This momentum is continuing into Q3 with order patterns remaining strong through July. Weakness in construction continued to impact our Diversified Industrials business during the quarter.”
- Nucor ($31.6B, Metals & Mining): “We continue to see solid and steady booking rates, and our steel mills backlog at the end of Q2 was up nearly 30% YoY. Our sheet backlog at the end of Q2 was 15% higher YoY. We continue to see strong demand as evidenced by robust coating activity and believe this reflects improved business confidence among our customers servicing the construction and infrastructure markets.”
- Steel Dynamics ($18.0B, Metals & Mining): “The underlying steel demand remains steady. However, customers continue to exercise caution in placing orders due to ongoing uncertainty related to trade policies and interest rates. Looking ahead, ongoing onshoring activities, recently announced domestic manufacturing projects, and continued infrastructure spending are expected to further support fixed asset investment and construction-related demand. In the energy sector, oil and gas activity remains steady with encouraging signs of increased demand. Additionally, solar is particularly strong currently as producers attempt to benefit from expiring incentives.”
- PPG Industries ($23.7B, Chemicals): “The most sensitive segment for us as it relates to the global macro is Industrial. In early April, we did see some customer concerns around tariffs. As we progressed through the quarter, we saw a normal order pattern return. No significant changes throughout the quarter in order patterns. A little softer in Europe than we wanted; some softening in Asia, to be expected. Beyond that, no significant impacts. We expect the back half of the year to offset what happened in Q1. As we exited the quarter on volumes, we didn’t see any pull-forward into Q2.”
- Packaging Corp of America ($17.4B, Containers & Packaging): “It was a very strong quarter. We fully realized our earlier announced price increase. While customer ordering patterns remain somewhat cautious, corrugated demand remained solid and steady throughout the quarter. There are still a lot of questions around tariffs and what’s happened globally. Everybody is waiting for something they can count on long term, so we’ve got a lot of customers who are managing their inventories very closely. We’re seeing some spikes and then some valleys in terms of ordering patterns, and we’ve got some segments that are off – automotive being one, and building products being off because of the housing market that’s basically stagnant.”
- Dow ($15.3B, Chemicals): “As we head into the back half…Dow and some of our industry peers are noting expectations that the global macroeconomic backdrop will remain challenged. Ongoing tariff and geopolitical uncertainty have impacted demand patterns, especially in the industrial, infrastructure, and durable goods sectors.”
- Reliance ($15.0B, Metals & Mining): “The tariff uncertainty has been holding back some of the buying by many customers. Once that gets unlocked, we feel very good about where we and the industry will go for the rest of the year or at whatever point tariffs get resolved. Encouraging trends in our key end markets, including signs of reshoring activity, are creating additional tailwindsas we look ahead.”
- Avery Dennison ($13.1B, Containers & Packaging): “While we’ve seen some signs of apparel industry improvement exiting Q2, the outlook remains uncertain and customer feedback and sentiment remains muted…we’re assuming a continuation of soft apparel volumes in Q3.”
- Crown Holdings ($11.5B, Containers & Packaging): We are starting to see some green shoots as people get more comfortable with the ongoing demand globally for more beverage cans and the need for more equipment. Despite all the noise in the economy, be it political or economics, the can continues to perform exceptionally well.”
- Westlake ($10.7B, Chemicals): “Pipe & Fittings sales volume growth benefited from increasing demand for municipal water applications, driven in part by spending from the 2021 Infrastructure Act. The significant underspend in water infrastructure in the U.S. and the funds from the IIJA should continue to provide a solid foundation for our Pipe & Fittings sales for many years. Building Products sales volume was lower YoY, reflecting the slowdown in North American residential construction.”
Tariffs & Trade Policy
Companies Offsetting Direct Impact with Surcharges and Supply Chain Shifts; Domestic Steel Sees More Favorable Backdrop, While Chemicals Contend with Anticompetitive Pricing in Some Non-U.S. Markets, and Broader Tariff-driven Demand Concerns Persist
- Ecolab ($74.9B, Chemicals): “During Q2, we began implementing our trade surcharge for all customers in the U.S. Given the dynamic international trade environment, the surcharge coupled with our world-class supply chain team enables us to reliably supply our customers while delivering value that exceeds the total price increases. With this now in place, we expect our total pricing to strengthen in Q3 and Q4.”
- PPG Industries ($23.7B, Chemicals): “We’re monitoring the tariff situation, and we’ll react accordingly with pricing actions and/or further self-help actions in order to mitigate any financial impacts. We have not experienced any significant change to our raw material pricing, and we expect low single-digit inflation for the year as our suppliers continue to favor volume over pricing.”
- Steel Dynamics ($18B, Metals & Mining): “Last fall, we and other industry participants initiated a trade case related to these products and have since received favorable preliminary countervailing and anti-dumping rulings. We anticipate final rulings to be determined before the end of September. This uniquely positions us as we are the largest producer of non-automotive coated flat rolled steel products in North America. Together with the announced Section 232 steel tariffs, these developments are expected to positively impact demand for lower carbon emission U.S. produced steel.”
- Dow ($15.3B, Chemicals): “Increasingly, we are seeing anticompetitive oversupply activities particularly when it comes to imports into Europe and Latin America. Our teams are actively engaged in these regions to aggressively defend our local asset footprint and to ensure that a fair-trade environment remains. We’re engaging in positive and productive conversations with the governments around the world as it relates to trade and tariff uncertainties, and we’re confident that we’re in a strong position to mitigate the impact.”
- Ball ($15.1B, Containers & Packaging): “As tariffs increase, that scrap market is going to increase at some point as well. It already has a bit. We’re keeping an eye out, but it hasn’t had a negative impact. We’re more concerned about the demand side of tariffs across the economy than we are about any isolated metal market at this point.”
- Reliance ($15.0B, Metals & Mining): “The tariffs and the unknown around the tariffs gave our suppliers an opportunity to increase prices on some products. On the other side, our customers also were facing that uncertainty. If they could hold back on buying, they were. So, it was a little more difficult to get the market to accept [announced price increases]. So, we were getting the higher cost metal more quickly. We’re working through that. We are positive on the price increases on aluminum and stainless flowing through and holding. It just takes a little time to get those in, which we expect to happen through Q3. Our customers who are purchasing aluminum are going to be paying a higher price. They may just buy a little less and a little more frequently.”
- Crown Holdings ($11.5B, Containers & Packaging): “The all-in cost of aluminum is close to an all-time high. We don’t believe we can afford to absorb any of that. Fortunately for us, our contracts allow for the pass-through. I’m sure our customers don’t believe they can afford to absorb it, so ultimately the cost of that is borne by the consumer. To date, we have not seen the consumer back off the purchase of beverage cans. Having said that, our customers are promoting, and into an increasing cost environment. Eventually, they’re going to be hit with higher cost. But we’re not hearing anything concerning.”
- Avery Dennison ($13.1B, Containers & Packaging): “Changes in trade policy throughout the quarter had both direct and indirect impacts. We successfully continue to mitigate the direct cost increases through strategic sourcing adjustments and select pricing surcharges, and to minimize the impact of sourcing demand reduction, particularly in apparel and general retail categories. Regarding raw material costs, higher tariffs, primarily between the U.S. and Europe, began affecting us in the middle of Q2, given that we had inventory on hand when the tariffs first went into effect. We will see some sequential inflation, given we’ll have a full quarter of the tariff impact in Q3, but we expect to offset that with surcharges and sourcing shifts.“
Expense Management
Cost Saving Programs in Full Effect: Several Expanding Capex Reductions and Restructuring Efforts to Offset Softer-for-Longer Demand
- PPG Industries ($23.7B, Chemicals): “We expect growing benefits from our aggressive self-help and discretionary cost management programs as we move forward through 2025 and beyond. The restructuring benefits we earmarked for this year were $75M. We’re about a $30M clip through the first half.”
- Dow ($15.3B, Chemicals): “In Q2, we progressed several near-term cash support levers. Additionally, we are accelerating progress on our $1B in cost savings actions, where we now expect to deliver approximately $400M this year. “
- Avery Dennison ($13.1B, Containers & Packaging): “We now expect restructuring savings net of transition cost of ~$50M as we continue to ramp up our productivity efforts. And given the volume environment, particularly in apparel and general retail, we’re continuing to do discretionary cost reductions – things like travel, etc.”
- Westlake ($10.7B, Chemicals): “During the first half of 2025, we achieved over $75M of company-wide cost reductions towards our full-year target of $150M to $175M. While we are pleased with this progress, given the protracted nature of the current downturn, we are expanding the scope and nature of our cost reduction efforts to target an additional $200M by 2026.”
- Eastman Chemical ($7.0B, Chemicals): “We are not operating in a robust demand environment, but we are laying the groundwork for a strong and steady growth engine, now and in the future. In this environment, we remain focused on controllable actions with an emphasis on cash generation with every lever of the company. We are reducing inventory by greater than $200M from current levels, keeping capital expenditures for full-year 2025 at ~$550M, and reducing costs by ~$75M net of inflation.”
- Cleveland-Cliffs ($4.8B, Metals & Mining): “We took actions during the quarter to lower both our SG&A run rate and capex budget. Our full-year 2025 expectations for these items were reduced by a combined $50M. These were proactive, surgical reductions based on our newly tightened footprint. Our overhead structure is now leaner, and we’re getting more out of every dollar we spend.”
- Cabot ($4.3B, Chemicals): “Given the weak macro environment and all the uncertainty from the tariff discussions, we’re working hard on the cost and procurement savings front, and all of that is showing through into strong results given the weak demand environment. Last quarter, we talked about fixed cost and procurement initiatives that we targeted at about $30M for the year. We’re trending a bit ahead of that. And some of those are structural. These would be a mix of items that include head count-related actions, things like timing or lower third-party spend. Those are the actions we’ve been taking to reduce costs. If the environment improved, you would probably see some of those costs come back in.”
- Ashland ($2.3B, Chemicals): “Our restructuring program remains ahead of schedule. We’re also making strong progress on our $60M manufacturing optimization program. We believe 2026 is still going to be a tough environment for a lot of industries, so we’re going to plan accordingly. Self-help is going to be a big part of our actions.”
- Olin ($2.1B, Chemicals): “We anticipate our efforts will result in 2025 year-end run rate cost savings of $70M to $90M. As part of our optimize the core strategic pillar, our Beyond250 cost program includes rightsizing…manufacturing facilities, accelerating a performance-driven culture, and leveraging continuous improvement and operational excellence initiatives.”
OBBBA Impact
Bonus Depreciation and R&D Expensing Seen Driving Cash Tax Benefits; Companies Note Potential to Spur Investment and Continue to Assess Full Implications
- Vulcan Materials ($37.4B, Construction Materials): “[Regarding OBBBA], there are certainly some benefits in there for us, mainly from the 100% bonus depreciation and the expensing of domestic research costs. We currently estimate a cash tax benefit of over $40M for June year-to-date activity and would expect the full-year benefit could approach $100M. We don’t expect any material impacts to our effective tax rate, but definitely a cash tax benefit for 2025 and going forward.”
- Nucor ($31.6B, Metals & Mining): “If I begin from the macro, the One Big Beautiful Bill comes into play, certainty regarding what the corporate tax rate is going to be. Now we can begin building certain things out. The other incentives for reshoring are there. Within that bill, you see $47B for funding for the border wall, $29B slated for shipbuilding. This bill is going to be very advantageous for the steel industry but also manufacturing as a whole. [Regarding direct tax benefits], it probably has the most pronounced effect for us in R&D spending and the ability to accelerate that into expensing rather than amortizing over seven years.”
- RPM International ($15.2B, Chemicals): “We are still sorting through [the bill]. In general, it’s good news that the corporate tax rate is not going to 28%, which was proposed in the last administration. Bonus depreciation should spur investment. From a tax perspective, it is looking like we can expense the purchase of tangible property at a 100%, not 40%, which was the case prior to January. Nothing but good news, but still a lot to sort through. Some of the positive impacts on manufacturing investment will get people off the sidelines in terms of making decisions on additional projects.”
- Ball ($15.1B, Containers & Packaging): “[Regarding OBBBA], we don’t think it’s going to change the trajectory much of the effective tax rate. Largely, the benefits are going to come in through the acceleration of depreciation and ability to deduct more because of the EBITDA limit versus the operating earnings limit. For the most part, we’re still early and really figuring it out, but I don’t think it’s going to be much of a change for us.”
- Scotts Miracle Gro ($3.5B, Chemicals): “I do want to address favorable tax implications resulting from the recently passed One Big Beautiful Bill signed into law. The restoration of these key TCJA provisions that include a bonus depreciation, R&D expensing, and increasing the deductible interest limitation will provide us with meaningful cash tax benefits going forward. These changes will allow us to drive further investment in our business for years to come.”
Around the World
Europe Weakness Continues, APAC and India Face Headwinds from Overcapacity, North America Stable but Softer, Latin America Holds Steady, and China a Question Mark
- International Paper ($24.3B, Containers & Packaging): “Industry demand in North America has been relatively stable, but softer than last year, as economic uncertainty from tariffs continued to impact industrial production and box demand across the manufacturing sector. Turning to EMEA, the weak market is a headwind for us with macroeconomic volatility in the region. While we’re holding market share, box shipments slowed sequentially in Q2 driven by market softness in April and May. June volumes, however, showed signs of recovery, which has continued into July.”
- PPG Industries ($23.7B, Chemicals): “Regionally, we delivered organic growth in both the U.S. and Latin America, with tepid demand in Europe and some softening in Asia. While volumes remained lower, we saw evidence of improvement in certain countries, albeit inconsistent. We delivered organic sales growth in Mexico, aided by solid retail sales, while results were impacted by the pause in project-related spending.”
- Packaging Corp of America ($17.4B, Containers & Packaging): “While domestic sales had been on plan, even with relatively low exposure to China and Europe, we’ve seen noticeably lower export sales with the global trade tensions overhanging the market.”
- Dow ($15.3B, Chemicals): “Polyethylene volumes were up led by the U.S. and Canada, confirming resilient demand in the region, but down in Asia-Pacific as tariff uncertainty limited exports early in the quarter. Lower Polyurethanes & Construction Chemicals volumes in EMEAI, where we continue to see increasing import activity from competitors in China, were partially offset by higher industrial solutions volume across data center cooling and gas treating Our industry continues to face difficult market dynamics in Europe, including an ongoing challenging cost and demand landscape.”
- Crown Holdings ($11.5B, Containers & Packaging): “The impact of tariffs on various Asian industries ultimately impacting consumer confidence and buying power. We don’t see destocking or any direct tariff impact in Europe. What we do continually see in Europe is a continuing contraction in the industrial economies. The challenge for anybody is when you’re selling into contracting economies, eventually the consumers become very concerned with their bank account level and the prospects of having a job.”
- Ashland ($2.3B, Chemicals): “We expected some recovery in the coatings market in the U.S. and Europe, which didn’t materialize. We’re going to plan conservatively on U.S. and Europe for next year, but we recognize that, given the pent-up demand if interest rates move, there is upside potential that will factor into our thinking. If you look at Latin America and Southeast Asia, they’re pretty stable right now. The big question is China. We’re assuming that’s not going to improve in the near term, and we’re acting appropriately. [In Specialty Additives], persistent overcapacity and weak demand in China continue to pressure both volume and pricing, intensifying competition across the region and in export markets like Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and India.”
In Closing
Our analysis finds the fundamentals of the Materials sector – a bellwether for the global economy – remain challenged as companies continue to operate in a landscape defined by persistent uncertainty, shifting global trade dynamics, and softer-for-longer demand dynamics. While select end markets are showing signs of stabilization and even strength, the sector as a whole continues to see choppy demand and uneven ordering patterns, exacerbated by high sensitivity to policy developments and other external factors.
Looking ahead, the sector’s trajectory hinges on several unresolved issues, including the path of global trade policy and interest rates, the pace of recovery in key regions like Europe and China, the ability to pass on higher costs related to tariff-induced inflation, and balancing cost discipline while investing for future growth. The recent passage of OBBBA tax legislation offers a potential tailwind for investment, but the full impact is still being assessed. As companies continue to navigate these crosscurrents, we’ll be watching for further signals of demand normalization and any shifts in sentiment as the macro picture takes shape through the second half.
In the meantime, we’ll be back next week with our Closing the Quarter piece to round out the Q2’25 earnings season, including key themes to monitor as we move into Q3.
- Calendar year reporters; as of August 7, 2025
